Arc Flash Analysis: The Hidden Costs of Non-Compliance

Arc flash hazard analysis is a critical safety requirement in managing electrical risks in the workplace. It involves a systematic study to identify potential arc flash hazards and implement safety measures to protect workers and equipment. Compliance with standards like NFPA 70E and IEEE 1584 is not just a regulatory requirement; it's a fundamental aspect of operational safety and financial management.
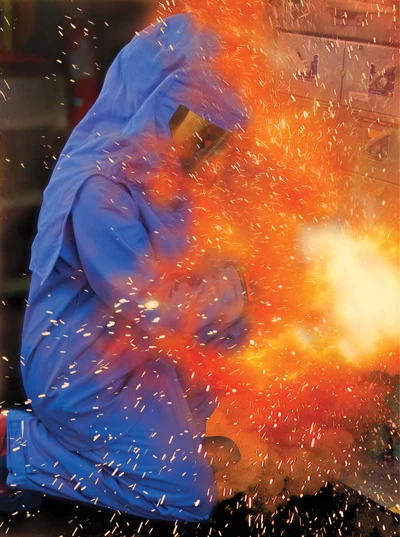
While the importance of arc flash hazard analysis may be well understood, the consequences of failing to conduct these assessments or neglecting their recommendations are often underestimated. Non-compliance carries a heavy price tag, encompassing both direct financial losses and severe implications for worker safety.
Visit Our Arc Flash Study Course
Direct Costs of Non-Compliance
The most obvious financial impact of non-compliance is the direct cost, including fines, penalties, and increased insurance premiums. Regulatory bodies can impose significant fines on organizations that fail to adhere to safety standards. Additionally, incidents resulting from non-compliance can lead to higher insurance premiums due to perceived increased risks.
Indirect Costs and Liability
Beyond fines, the indirect costs of non-compliance can be substantial. These include litigation costs, compensation claims, and the potential for civil lawsuits following an arc flash incident. If an employee is injured due to a lack of proper hazard analysis and safety measures, the employer could be held liable for damages, leading to costly legal battles and settlements.
Direct Financial Costs
- Medical Expenses: Arc flash survivors often face lengthy hospitalizations, surgeries, and rehabilitation. According to NFPA statistics, the average medical cost for a worker surviving a severe arc flash event is approximately $1.5 million. These expenses often fall on the employer through workers' compensation insurance.
- Fines and Penalties: Regulatory bodies like OSHA impose substantial fines on organizations that violate electrical safety standards. Failure to implement an arc flash hazard program or provide appropriate PPE can lead to penalties in the hundreds of thousands of dollars.
- Equipment Damage: The explosive force of an arc flash can irreparably damage electrical equipment. The cost of replacing switchgear, transformers, and other components can easily reach six- or even seven-figure sums.
- Lost Productivity and Downtime: Arc flash incidents often force temporary facility closures. Production downtime, missed deadlines, and recovery efforts translate to a significant loss of revenue and potential damage to a company's reputation.
Human Costs and Safety Implications
- Severe Injuries and Fatalities: The most devastating consequence of non-compliance is the potential for severe injuries or fatalities. Arc flash events inflict burns, blindness, hearing damage, and internal injuries – the physical and psychological trauma can be lifelong.
- Loss of Skilled Personnel: The impact of losing an experienced electrician or technician extends beyond the human cost. Replacing those workers is time-consuming and costly, further burdening the organization.
- Damaged Morale and Safety Culture: Serious workplace accidents can create an atmosphere of anxiety and fear among workers, undermining trust and hindering safety-focused performance.
Proactive Investment vs. Cost of Neglect
The cost of a comprehensive arc flash hazard analysis pales in comparison to the potential expenses resulting from non-compliance. The following are core components typically included in an arc flash study:
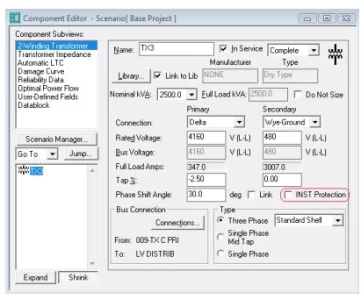
- Detailed Data Collection: Gathering system specifications, protective device ratings, and creating accurate system models.
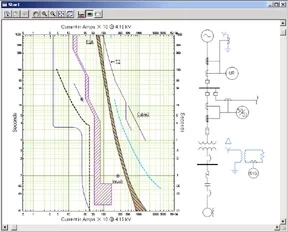
- Incident Energy Calculations: Determining the potential heat energy released during an arc flash event.
- Arc Flash Boundary Definition: Establishing safe working distances based on the calculated incident energy level.
- PPE and Safety Recommendations: Specifying the appropriate protective gear and outlining safe work procedures.
Beyond Compliance: Long-Term Benefits
- Informed Risk Management: Arc flash hazard analysis data enables organizations to make strategic decisions about electrical infrastructure upgrades, prioritizing worker safety.
- Demonstrated Safety Commitment: Investing in hazard analysis showcases a responsible approach to safety, building confidence among workers and stakeholders.
- Potential Insurance Savings: Some insurance providers may offer reduced premiums to organizations that proactively manage arc flash risks.
Conclusion
Addressing arc flash hazards is not merely a regulatory obligation; it is a sound business practice and a moral responsibility. The hidden costs of non-compliance, in terms of financial losses, human suffering, and diminished operational capacity, far outweigh the investment required for proper assessment and risk mitigation. By adopting a proactive stance towards electrical safety, organizations can protect their most valuable assets – their workers – while simultaneously safeguarding the long-term viability of their operations.